Analysis of the heat conduction mechanism of Liquid Cold Plate
Release time:
2025-04-30 16:00
source:
As an efficient heat dissipation component, the heat conduction mechanism of Liquid Cold Plate involves the synergistic effect of multiple physical processes.
First, inside the Liquid Cold Plate, the heat conduction starts from the heat source contacting the surface of the Liquid Cold Plate. When the heat source contacts the surface of the Liquid Cold Plate, the heat is transferred through the solid part of the Liquid Cold Plate in the form of heat conduction. Liquid Cold Plate is usually made of materials with good thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum. Driven by the temperature difference, the free electrons in these metal materials move in a directional manner, transferring heat from the high temperature area to the low temperature area, which is the microscopic mechanism of solid heat conduction.
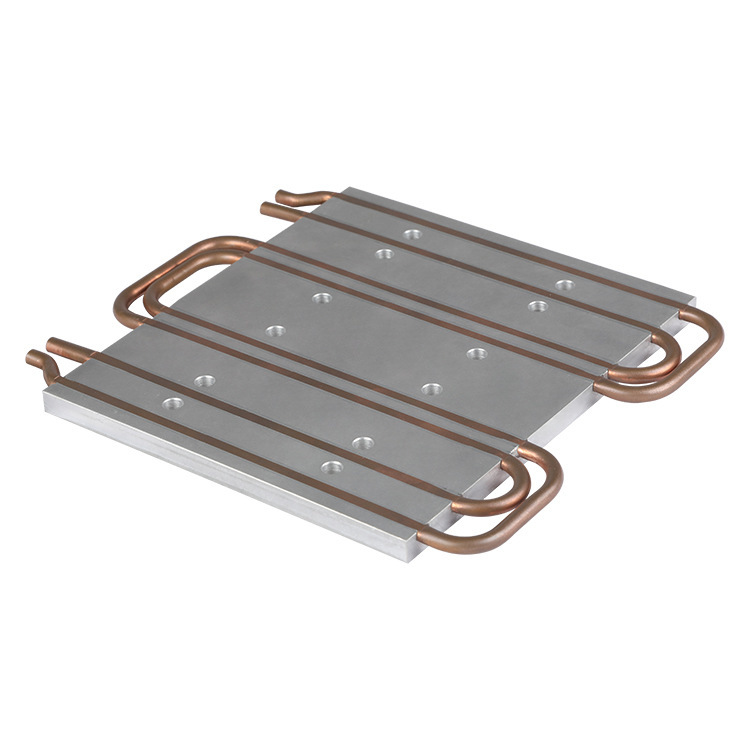
Next, the microchannel or flow channel structure inside the Liquid Cold Plate plays a key role. When the heat is conducted to the vicinity of the flow channel, the heat is transferred to the coolant in the flow channel. The coolant flows in the flow channel to form forced convection. This forced convection greatly enhances the heat transfer efficiency. According to Newton's law of cooling, the heat transfer rate of convective heat transfer is related to the flow rate, temperature difference and convective heat transfer coefficient of the fluid. In the Liquid Cold Plate, the rapid flow of the coolant allows it to quickly take away heat. The coolant molecules and the wall of the flow channel continuously exchange heat, transferring heat from the wall to the main part of the coolant.
Then, the heated coolant will bring the heat to the heat dissipation area of the Liquid Cold Plate. In this area, the heat will be dissipated to the surrounding environment by conduction and convection, such as dissipating the heat into the air through the heat dissipation fins. If the surrounding environment is assisted by an air cooling system, the natural or forced convection of the air will further accelerate the dissipation of heat, thus completing the entire heat conduction and convection heat dissipation cycle.
The heat conduction mechanism of the Liquid Cold Plate is a multi-step, multi-heat transfer method coordinated process. Its efficient heat dissipation capacity makes it play an irreplaceable role in many fields such as electronic equipment heat dissipation.
Blog
detail
Unlocking Efficiency: The Essential Guide to Flat Aluminum Heat Pipes
Discover key considerations for using flat aluminum heat pipes effectively in your applications.
Chill Out: The Ins and Outs of a Liquid Cooling System
Discover the key considerations for installing and maintaining a liquid cooling system for optimal performance.
Chill Out: Navigating the Ins and Outs of Cold Plate Liquid Cooling
Discover essential tips and considerations for effective cold plate liquid cooling systems.
Analysis of the heat conduction mechanism of Liquid Cold Plate
As an efficient heat dissipation component, the heat conduction mechanism of Liquid Cold Plate involves the synergistic effect of multiple physical processes.
Unleashing the Power of Flat Aluminum Heat Pipes in Modern Industries
Discover how flat aluminum heat pipes enhance efficiency across various industries. Learn their applications and benefits!
Cool Down: The Game-Changer of Liquid Cooling Systems
Discover the transformative impact of liquid cooling systems in various industries and how they enhance efficiency.